AR in the classroom – A device is born
Firstly, let me introduce myself – I’m Melanie Collins, Head of Geography at a school for girls in the South East of England. I’ve been in this role for quite some years now but, like Geography itself, the role is ever changing and I am constantly looking for new ways to keep myself challenged and, quite simply ‘GeoAwesome’.
My interest in the use of technology in Geography began many, many years ago. I can remember back to a time around 1984, or thereabouts, when my father (an industrial systems computer manager) came home with a ‘surprise’ family present for Christmas. I remember the excitement on opening the package only to feel somewhat deflated when it turned out to be an ‘Acorn Electron’ computer than he’d managed to pick up for £99 “with 5 free games”. As a 12 year old girl I was far from impressed. Nevertheless, in the months that followed, one particular DOS game ‘Sphinx Adventure’ got me thinking about the power of technology in helping me understand more about how we see places. The game itself was not exciting and involved typing in instructions to take us from one place in the game to another to solve the ‘mystery’ but the mental mapping involved was a revelation and I really do think it was this that paved my career path. I went on to play more games like this over the years and loved the associated spatial representations of place, even if these were just my own.
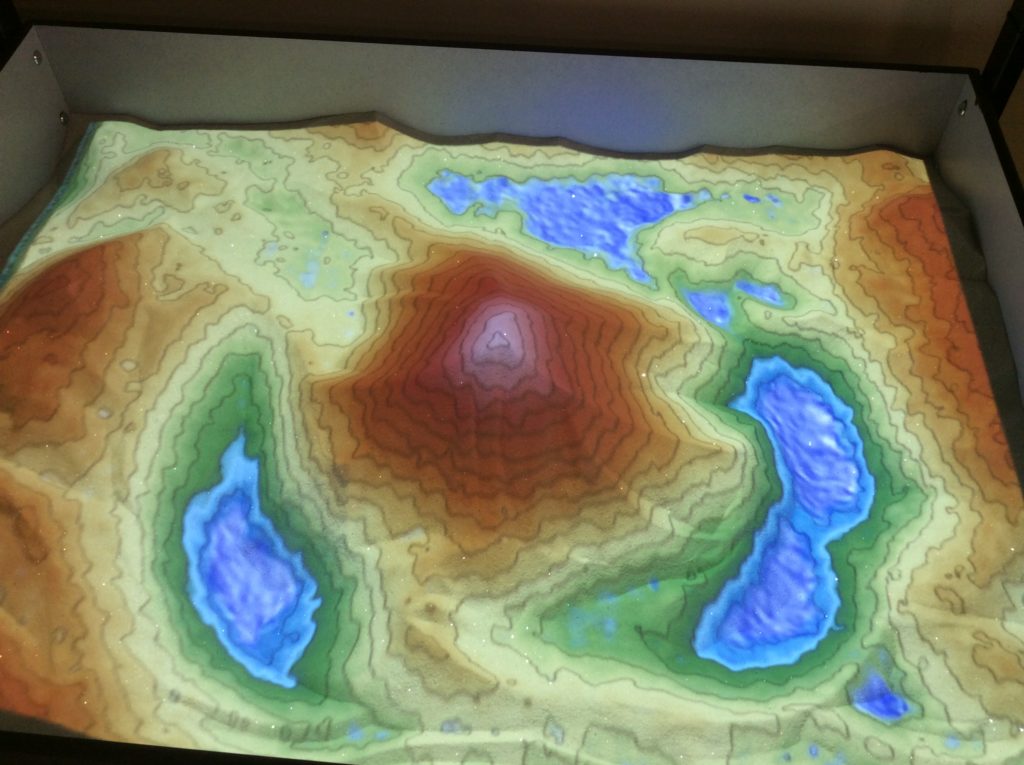
Years later and I have been an avid user of technology in the classroom but perhaps one thing that has recently been a ‘game changer’ in my classroom has been the addition of an Augmented Reality Sand Box. Now, I appreciate that you can go to various museums and universities all over the world to see these but having one in the classroom is a bit of a luxury. I can boast that my classroom was the first in the UK to have one of these awesome devices – not because we have shed loads of available cash to spare but because of a little teamwork and being resourceful.
Rewind to the summer of 2015 and our school Network Manager – a self confessed ‘geo nerd’ – showed me an extract from a website https://arsandbox.ucdavis.edu/ and YouTube posts https://www.youtube.com/channel/UCy-htpQJxUJ0pkJ9C9Y5MqA and I remember saying ‘I want one of those!’ It soon came to be that my wish became a command and IT ‘geo nerd’ got working with our Head of Design Technology and I to discuss the way forward. I wanted to create a virtual landscape, complete with contours, to simulate features such as river valleys and help students learn more about relief.
The sandbox uses a propriety Linux based Vrui VR development toolkit, developed at the University of California, Davis https://arsandbox.ucdavis.edu/instructions/ and an old Kinect 3D video processing framework, picked up second hand from eBay. The AR Sandbox uses the 3D camera qualities afforded by the Microsoft Kinect to scan the 3D shape of the sand surface in real time, and additionally to detect hand gestures above the surface to create ‘virtual rain clouds.’ A computer collects data from the camera, and creates a real-time dynamic topographic map. A projector, also mounted above the sandbox, projects that topography map back onto the real sand, calibrated such that real and virtual features line up exactly.
We were on a fairly tight budget but the computer required to run the sand box had to be of high specification with regard to processing power and memory and a 3D accelerated graphics card was also needed to handle the effects of the water and lava (another feature I had never imagined would be possible to show on this virtual landscape). I understand that the specification of the computer can be reduced assuming one does not want to use the environmental features of the sand box but there’s no point having half the fun! The construction for the sand box was made to the required specifications of myself and the students. In my case I needed something that could be transported to other areas of the school if necessary and also large enough to have a group of students stand around and use it. We also needed to consider the materials used to construct the sand box due to the weight of the sand also the consideration of water use to make the sand more suitable for sculpting landscapes. The sand used was a very fine white play sand, chosen due to its light reflective properties. This wasn’t cheap and admittedly dust does need to be controlled, but we made a great saving by making the base out of an old shower unit from our PE department!
In the construction phase we had great fun trialling with white sheets but once we had the sand in place it was time to ‘switch her on’ and get using this great resource we had built. Gasps of ‘wow’ and ‘how does it do that?’ were heard from the students and staff that had come to see the ‘new geoawesome baby’ that now lay at the back of my classroom.
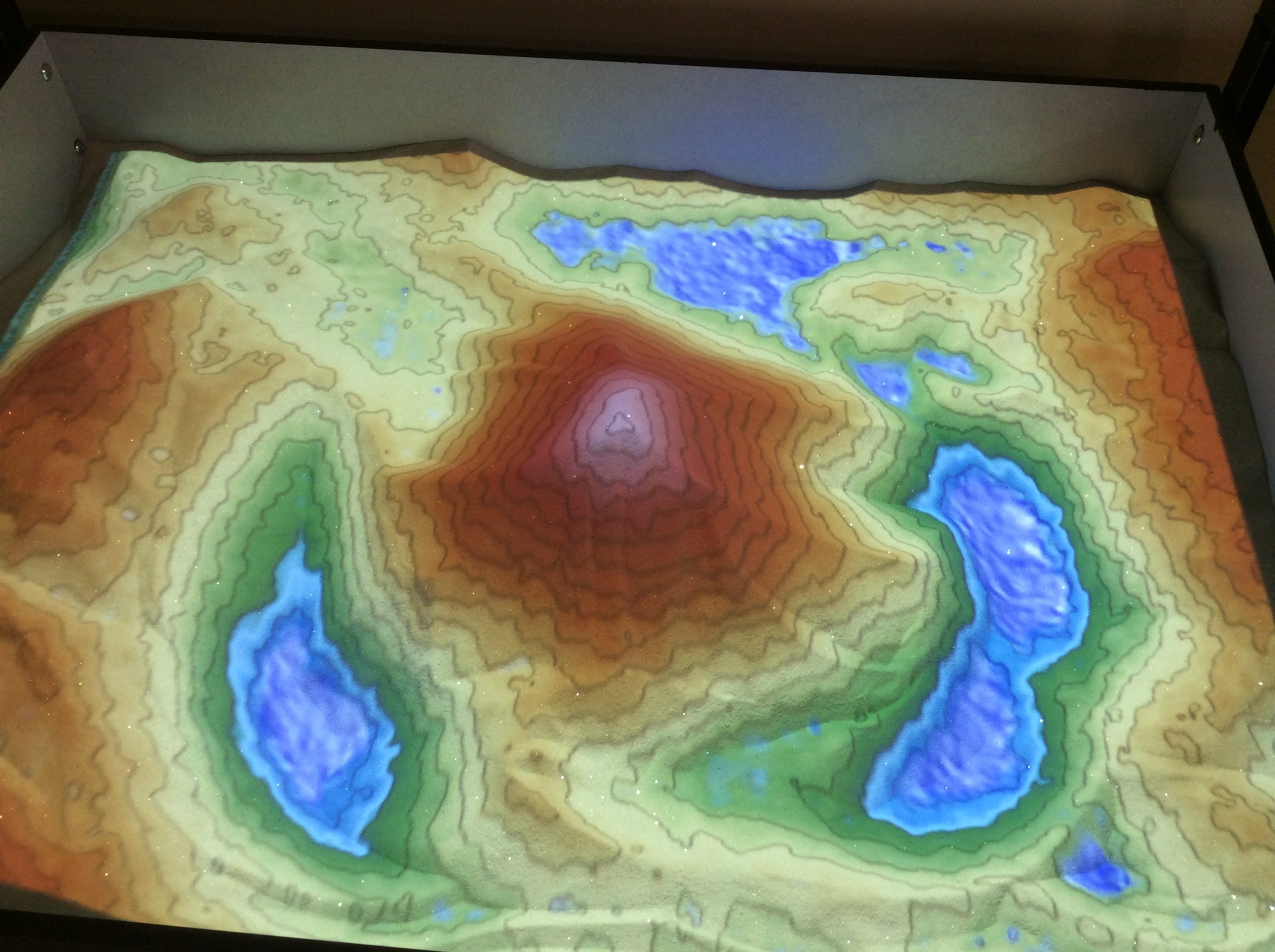
The AR sandbox in action
As a parent, I know only too well that the birth is perhaps the easy part – what you do after that point is what really matters and that’s where I will pick up next time.